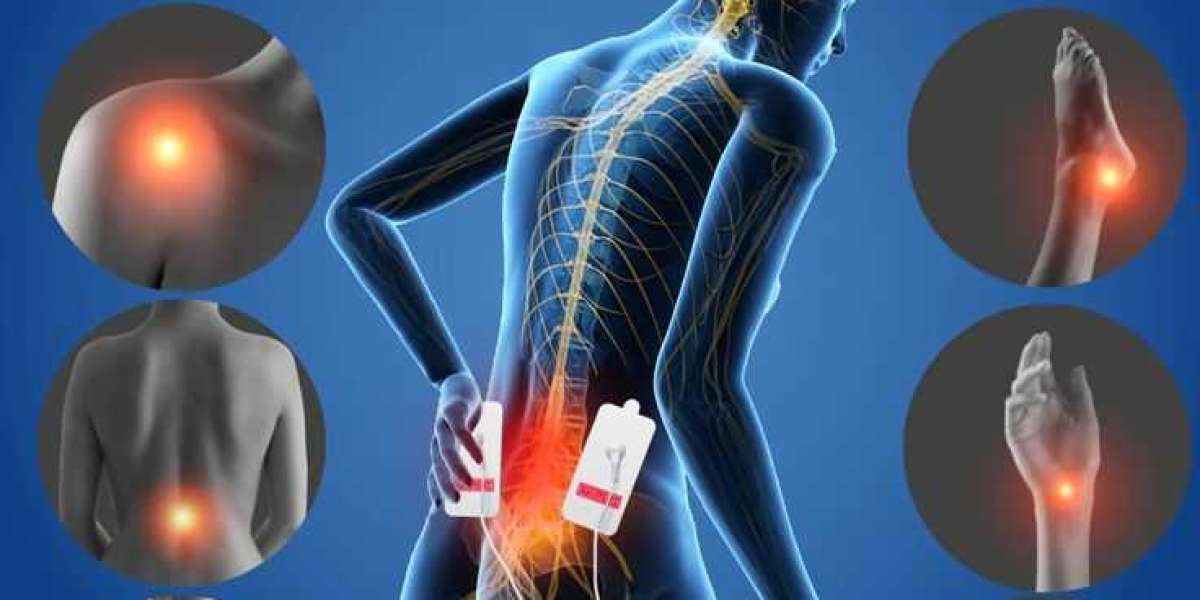
Nerve Function: Nerves serve as messengers in the body, transmitting signals between the brain, spinal cord, and various parts of the body. Sensory nerves carry signals related to touch, temperature, and pain from the body to the brain, while motor nerves transmit signals from the brain to muscles to control movement.
Nervigesic 300mg Pregabalin is use to alleviate nerve pain brought on by spinal cord injury, shingles, and diabetes. The drug pregabalin works by altering the manner in which nerves transmit impulses to the brain.
Neuropathy: Neuropathy occurs when there is damage or dysfunction to the nerves. This damage can result from various factors, including injury, infection, metabolic disorders like diabetes, autoimmune diseases, and exposure to toxins or certain medications.
Altered Nerve Signaling: In neuropathic pain, nerve damage disrupts the normal transmission of signals between the peripheral nerves (those outside the brain and spinal cord) and the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord). This disruption can lead to abnormal signaling, causing sensations of pain, tingling, numbness, or weakness.
Hyperexcitability: Nerve damage can lead to hyperexcitability of nerves, where they become overly sensitive and respond abnormally to stimuli. This heightened sensitivity can cause pain sensations even in response to normally non-painful stimuli, a phenomenon known as allodynia.
Spontaneous Activity: Nerve damage can also result in the generation of spontaneous electrical impulses along the nerves, even in the absence of external stimuli. This spontaneous activity can contribute to sensations of burning, shooting, or stabbing pain, even at rest.
Central Sensitization: In some cases of neuropathic pain, prolonged nerve damage can lead to changes in the central nervous system, resulting in a phenomenon called central sensitization. In central sensitization, the brain and spinal cord become hyperresponsive to pain signals, amplifying the perception of pain and contributing to chronic pain conditions.
Neuroplasticity: The nervous system has the ability to adapt and change in response to injury or disease through a process called neuroplasticity. In neuropathic pain, neuroplastic changes may occur in both the peripheral and central nervous systems, altering the way pain signals are processed and perceived.
Understanding the connection between nerve dysfunction and neuropathic pain is essential for developing effective treatments. By targeting the underlying mechanisms of nerve damage and abnormal signaling, healthcare providers can help manage neuropathic pain and improve patients' quality of life. Treatment approaches may include medications, physical therapy, nerve blocks, lifestyle modifications, and complementary therapies aimed at reducing pain and improving nerve function.